FUNCIONES POLINÓMICAS DE SEGUNDO GRADO
-
Upload
indigo-shepard -
Category
Documents
-
view
52 -
download
4
description
Transcript of FUNCIONES POLINÓMICAS DE SEGUNDO GRADO

FUNCIONES POLINÓMICAS DE SEGUNDO GRADO

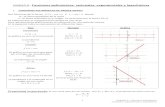
Confeccionamos la tabla de valores para la función f: / f(x) = x2
x f(x) = x2
-4 16-3,5 12,25-3 9
-2,5 6,25-2 4
-1,5 2,25-1 1
-0,5 0,250 0
0,5 0,251 1
1,5 2,252 4
2,5 6,253 9
3,5 12,254 16

Graficamos los puntos obtenidos en la tabla anterior:

Unimos los puntos obtenidos:
f(x) = x2

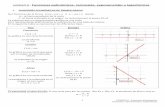
Con los valores de x usados anteriormente, realizamos la tabla de valores para la función: f: / f(x) = x2 + 1
x f(x) = x2 x f(x) = x2 + 1-4 16 -4 17
-3,5 12,25 -3,5 13,25-3 9 -3 10
-2,5 6,25 -2,5 7,25-2 4 -2 5
-1,5 2,25 -1,5 3,25-1 1 -1 2
-0,5 0,25 -0,5 1,250 0 0 1
0,5 0,25 0,5 1,251 1 1 2
1,5 2,25 1,5 3,252 4 2 5
2,5 6,25 2,5 7,253 9 3 10
3,5 12,25 3,5 13,254 16 4 17

Graficamos los puntos obtenidos en un mismo sistema de ejes cartesianos:

f(x) = x2
f(x) = x2+1Se obtienen las gráficas:

x f(x) = x2 - 4-4 12
-3,5 8,25-3 5
-2,5 2,25-2 0
-1,5 -1,75-1 -3
-0,5 -3,750 -4
0,5 -3,751 -3
1,5 -1,752 0
2,5 2,253 5
3,5 8,254 12
Vamos a graficar ahora la función : : f: / f(x) = x2 – 4Se utiliza la siguiente tabla de valores:

Se grafican en un mismo sistema de ejes cartesianos los puntos obtenidos en la tabla anterior y los usados para la función f(x) = x2

Las gráficas correspondientes son:
f(x) = x2 - 4
f(x) = x2

Se grafican en el mismo sistema coordenado las 3 funciones:f(x) = x2
f(x) = x2 -4
f(x) = x2+1

Consideremos ahora la función: f: / f(x) = -1x2 +4Se confecciona la tabla de valores:
x f(x) = x2 - 4 x f(x) = -1x2 + 4-4 12 -4 -12
-3,5 8,25 -3,5 -8,25-3 5 -3 -5
-2,5 2,25 -2,5 -2,25-2 0 -2 0
-1,5 -1,75 -1,5 1,75-1 -3 -1 3
-0,5 -3,75 -0,5 3,750 -4 0 4
0,5 -3,75 0,5 3,751 -3 1 3
1,5 -1,75 1,5 1,752 0 2 0
2,5 2,25 2,5 -2,253 5 3 -5
3,5 8,25 3,5 -8,254 12 4 -12

Las gráficas que se obtienen son:
f(x) = x2 - 4
f(x) = -1x2 + 4

f(x) = x2
f(x)= 3x2
Veamos otros ejemplos:

f(x) = x2
f(x)=x2 + 2x + 1

f(x)= -1x2 + 5x - 4

CONCLUSIONES:
• Las funciones polinómicas de segundo grado son de la forma: f: / f(x) = ax2 + bx + ccon a, b y c: N°s reales y a≠0
• En todos los casos la gráfica de la función es una parábola cuyo eje es una recta paralela al eje de las ordenadas.
•La función puede tener dos, una o ninguna raíz.
• Si a > 0, se dice que la función tiene “Concavidad positiva”• Si a < 0, entonces la función tiene “Concavidad negativa”