Hola mundo
-
Upload
ariadnitaa -
Category
Documents
-
view
753 -
download
2
description
Transcript of Hola mundo

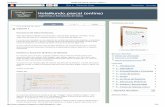
Hola Mundo

Código
public class HolaMundo {
public static void main() {
System.out.println("Hola Mundo");
}
}

Ejecución del Código
en Jeliot

1.- Se activa el área de métodos “main” y se reserva un
espacio en memoria para los métodos.
public static void main() {}
main
memoria

2.-“System.out.println”, muestra el mensaje “Hola
Mundo” y realiza un salto de línea a nivel de memoria.
System.out.println("Hola Mundo");
memoria
Hola Mundo
¶

3.-Se muestra el mensaje al usuario al mandarlo imprimir
con “System.out” obteniendo en este caso la cadena del
mensaje.
4.-Se finaliza la ejecución del programa y se cierra el
“main”.

Lista de términos
O public: da acceso a las variables o métodos y define a nuestra clase como publica.
O static: nos indica que es estático y solo puede haber una copia de este en memoria y no hay posibilidad de instanciar otro.
O Void; un tipo de dato que se utiliza para indicarle a un función que no devuelva parámetros
O System.out.println; método con el que se imprime el resultado.

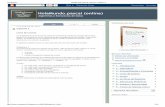
Lectura de
Datos desde el
Teclado

Código
import jeliot.io.*;
public class LecturaDeDatos {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = Input.readString();
char c = Input.readChar();
int i = Input.readInt();
double d = Input.readDouble();
System.out.println(s);
Output.println(c);
}
}

Ejecución del Código
en Jeliot

import jeliot.io.*;
public class LecturaDeDatos {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = Input.readString();
char c = Input.readChar();
int i = Input.readInt();
double d = Input.readDouble();
System.out.println(s);
Output.println(c);
}
}
1.-La ejecución comienza con el método “main”

import jeliot.io.*;
public class LecturaDeDatos {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = Input.readString();
char c = Input.readChar();
int i = Input.readInt();
double d = Input.readDouble();
System.out.println(s);
Output.println(c);
}
}
2.- Comienza la lectura de los datos.

import jeliot.io.*;
public class LecturaDeDatos {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = Input.readString();
char c = Input.readChar();
int i = Input.readInt();
double d = Input.readDouble();
System.out.println(s);
Output.println(c);
}
}
3.-
a)Se declara una variable de tipo String
b)se realiza la petición de datos
c)imprime el resultado.
a)
b)
c)

import jeliot.io.*;
public class LecturaDeDatos {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = Input.readString();
char c = Input.readChar();
int i = Input.readInt();
double d = Input.readDouble();
System.out.println(s);
Output.println(c);
}
}
4.-
a)Se declara una variable de tipo char
b)se realiza la petición de datos
c)imprime el resultado.
a)
b)
c)

import jeliot.io.*;
public class LecturaDeDatos {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = Input.readString();
char c = Input.readChar();
int i = Input.readInt();
double d = Input.readDouble();
System.out.println(s);
Output.println(c);
}
}
5.-
a)Se declara una variable de tipo entero
b)se realiza la petición de datos
c)imprime el resultado.
a)
b)
c)

import jeliot.io.*;
public class LecturaDeDatos {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = Input.readString();
char c = Input.readChar();
int i = Input.readInt();
double d = Input.readDouble();
System.out.println(s);
Output.println(c);
}
}
6.-
a)Se declara una variable de tipo entero
b)se realiza la petición de datos
c)imprime el resultado.
a)
b)
c)
Termina la ejecución del main

import jeliot.io.*;
public class LecturaDeDatos {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = Input.readString();
char c = Input.readChar();
int i = Input.readInt();
double d = Input.readDouble();
System.out.println(s);
Output.println(c);
}
}
7.-
a) Con el “System.out.println” se imprime el valor de la
variable s
b) Con “Output.println” se imprime el valor de la variable c
a)
b)
Termina ejecución del main

Lista de Términos
O Input.readString
O Input.readChar
O Input.readInt
O Input.readDouble
O buffer reador
O reader*
O filter reader
O piped reader
O string reader
O input steam reader
O file reader

Elaborado por:
O Judith Guzmán Ortiz.
O Ilse Ariadna Canales Nava.
O Martha Fabiola Robles Reyes.
O Karina Ruiz Ángeles.